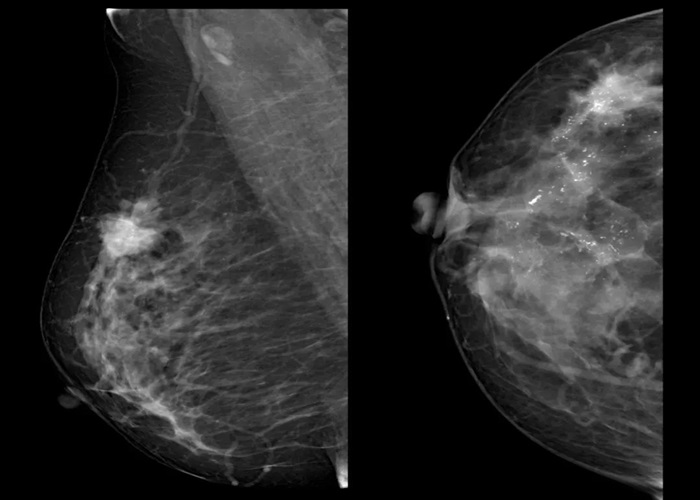
Breast cancer is a major global health challenge affecting women of all ages and backgrounds. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), breast cancer accounts for nearly 1 in 4 cancer cases among women worldwide, making it the most common cancer among women.
In 2020, an estimated 2.3 million new cases of breast cancer were diagnosed worldwide, with the disease causing significant morbidity and mortality. Breast cancer is a complex disease with multiple risk factors, including age, family history, reproductive factors, and lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption and physical inactivity.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has released new guidelines calling for a comprehensive approach to the control of breast cancer. The guidelines emphasize the importance of early detection, accurate diagnosis, and timely treatment, as well as the need for a multidisciplinary approach that includes patient education, psychosocial support, and palliative care.
According to the WHO, breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases diagnosed in 2020. While significant progress has been made in the prevention, early detection, and treatment of breast cancer, the disease remains a major public health challenge, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where access to screening and treatment is limited.
The new guidelines aim to address these challenges by providing evidence-based recommendations for the prevention, early detection, diagnosis, treatment, and palliative care of breast cancer. The guidelines also emphasize the importance of a patient-centered approach that takes into account the individual needs and preferences of each patient.
“Breast cancer is a major public health challenge, and we need a comprehensive approach to address it,” said Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director-General of the WHO. “These new guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations for the prevention, early detection, diagnosis, treatment, and palliative care of breast cancer, and emphasize the importance of a patient-centered approach.”
The new guidelines come as the global community marks Breast Cancer Awareness Month in October. The WHO encourages women to take advantage of screening programs and to seek medical attention if they notice any changes in their breasts.
Breast cancer is a growing health concern in China, with an estimated 2.5 million women living with the disease. However, a recent survey conducted by the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association (CACA) shows that attitudes towards breast cancer awareness and prevention are positive among the Chinese population.
The survey, which involved over 10,000 participants from across China, found that 80% of respondents believed that breast cancer was preventable, and 90% believed that early detection was key to successful treatment. The survey also revealed that 70% of respondents had received information about breast cancer through various channels, including social media, television, and healthcare professionals.
The CACA emphasizes the importance of continued education and awareness-raising efforts to reduce the burden of breast cancer in China. The organization also stresses the need for increased investment in breast cancer research and the development of new and effective treatments.
Read more:
Italy passes right to be forgotten for cancer survivors
WHO Guidelines Call For Increased Access To Over-The-Counter Contraception
Rise In Bird Flu Cases Among Humans Sparks Health Concerns Nationwide