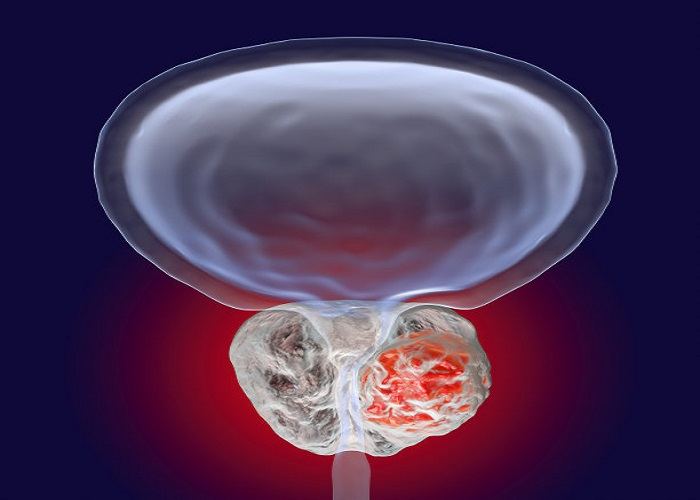
An enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition among older men. One question that often arises is whether this condition can cause bowel problems. Understanding this potential relationship is crucial for men’s health.
There are various research institutions and individuals that may publish research reports on the relationship between an enlarged prostate and intestinal problems.
For example, the research teams in the urology or related departments of universities like Stanford University, the University of Pennsylvania, etc. might conduct and publish such research as they are involved in urological and related health research.
Journals dedicated to urology, gastroenterology, or general medical research may publish relevant studies. Researchers from different institutions submit their findings to these platforms for publication.
The prostate gland is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. When the prostate enlarges, it can push against the rectum. In some cases, this pressure can lead to symptoms such as a feeling of incomplete bowel emptying. The prostate’s proximity to the rectum means that any increase in its size can potentially affect the normal functioning of the bowel.
However, it’s important to note that not all men with an enlarged prostate will experience bowel problems. The degree of prostate enlargement and the individual’s anatomy can play a significant role. Some men may have more space between the prostate and the rectum, reducing the likelihood of pressure – related issues.
In addition, other factors can contribute to bowel problems in men with an enlarged prostate. For example, medications used to treat BPH may have side effects that affect the bowel. Alpha – blockers, which are commonly prescribed to relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, can sometimes cause diarrhea or constipation in some patients.
Another aspect to consider is that some of the symptoms associated with an enlarged prostate, such as urinary frequency and urgency, can indirectly impact bowel habits. For instance, frequent trips to the bathroom for urination may disrupt normal bowel routines, leading to changes in bowel movements.
Moreover, men with an enlarged prostate may also have other underlying health conditions that can cause bowel problems. Conditions like diabetes, which can affect nerve function in the bowel, or other gastrointestinal disorders may be present simultaneously.
Medical professionals use various methods to assess the potential connection between an enlarged prostate and bowel problems. Physical examinations, including digital rectal exams, can help determine if the prostate is enlarged and if it is putting pressure on the rectum. Imaging studies such as ultrasounds or MRI scans may also be used to get a better view of the prostate’s size and its relationship to surrounding structures.
In conclusion, while an enlarged prostate can potentially cause bowel problems due to its anatomical location and the pressure it may exert on the rectum, the relationship is complex. It’s essential for men with an enlarged prostate to communicate any changes in bowel habits to their healthcare providers to ensure proper diagnosis and management.
Read more
- The Concern About Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Cross – Country Perspective
- Healthcare Products: Captivating Consumers Worldwide
- Countries’ Focus On Gastric Cancer: Treatment Approaches In The Spotlight