Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) manifests in various forms, and one of the lesser-known but equally distressing subsets is OCD related to breathing. Individuals grappling with this particular manifestation find themselves trapped in a relentless cycle of anxious thoughts and compulsive behaviors centered around the act of breathing. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on understanding, managing, and ultimately overcoming OCD breathing.
Understanding OCD Breathing
OCD, characterized by intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors, can extend its influence to various aspects of life, including seemingly automatic processes like breathing. Those with OCD breathing may experience obsessive thoughts about their breath, fear of not breathing properly, or concerns about the consequences of not paying constant attention to their breathing patterns. This heightened focus can lead to increased anxiety, creating a vicious cycle that reinforces the obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Before delving into strategies for overcoming OCD breathing, it is crucial to recognize the symptoms associated with this manifestation. Individuals may exhibit behaviors such as constant monitoring of their breathing, repetitive breath counting, or an intense fear of suffocation. Physical symptoms can include shallow or rapid breathing, dizziness, and heightened levels of anxiety. Identifying these signs is the first step towards addressing the issue effectively.
Seeking Professional Help
The complexity of OCD breathing necessitates a multidimensional approach to treatment. Consulting with a mental health professional, preferably one specializing in OCD, is paramount. Therapists can employ various evidence-based techniques, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP), tailored to address the specific challenges posed by OCD breathing. Medication, in conjunction with therapy, may also be recommended in severe cases to alleviate symptoms and support the therapeutic process.
Developing a Therapeutic Alliance
Building a strong therapeutic alliance with a mental health professional is foundational to successful treatment. Patients must feel understood and supported in their journey to overcome OCD breathing. Therapists, in turn, play a crucial role in guiding individuals through the process of challenging irrational thoughts, exposing them to anxiety-inducing situations gradually, and fostering resilience in the face of discomfort.
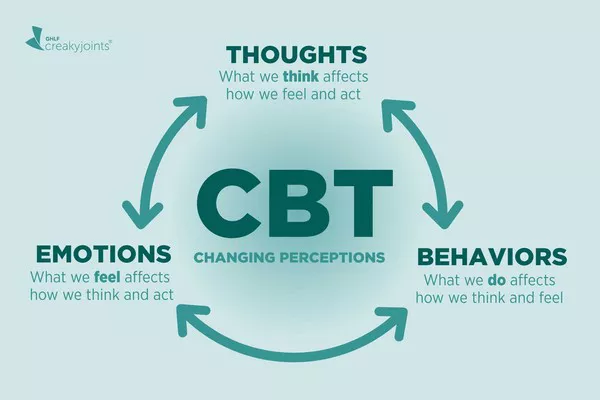
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Techniques
CBT has proven to be highly effective in treating OCD, including its various manifestations. The cognitive component involves identifying and challenging irrational thoughts related to breathing, while the behavioral component focuses on modifying maladaptive behaviors. Techniques such as cognitive restructuring, thought records, and behavioral experiments can be invaluable in reprogramming thought patterns and breaking the cycle of obsessive thoughts and compulsions.
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
ERP is a specialized form of CBT that specifically targets obsessive-compulsive behaviors. For individuals struggling with OCD breathing, exposure exercises involve deliberately exposing themselves to situations that trigger anxiety about breathing while refraining from engaging in compulsive behaviors. This systematic desensitization helps rewire the brain’s response to perceived threats, gradually diminishing the intensity of obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques into the treatment plan can provide individuals with tools to manage anxiety associated with OCD breathing. Mindful breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery are examples of techniques that can help individuals regain a sense of control over their breath and reduce the overall anxiety level.
Building a Support System
Overcoming OCD breathing is a challenging journey, and having a robust support system is instrumental in achieving success. Friends, family, and support groups can offer understanding, encouragement, and a non-judgmental space for individuals to share their experiences. Establishing open communication channels with loved ones ensures that they are well-informed about the challenges posed by OCD breathing and can provide empathetic support.
See Also:8 Effective Therapies for Managing OCD
Self-Care Practices
In addition to formal therapeutic interventions, integrating self-care practices into daily life is essential for managing OCD breathing. Adequate sleep, regular exercise, a balanced diet, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation contribute to overall well-being. These practices create a foundation for resilience, making it easier for individuals to cope with the challenges posed by OCD.
Challenging Negative Beliefs
OCD breathing often stems from negative beliefs about the consequences of not paying constant attention to one’s breath. Identifying and challenging these irrational beliefs is a crucial step in the recovery process. Therapists can guide individuals in recognizing the cognitive distortions that fuel obsessive thoughts, empowering them to reframe their perspectives and develop a more balanced view of their breathing.
Gradual Exposure and Goal Setting
Setting realistic goals for overcoming OCD breathing is crucial for long-term success. Gradual exposure to anxiety-provoking situations, coupled with the establishment of achievable milestones, allows individuals to make steady progress. Celebrating small victories along the way reinforces a sense of accomplishment and motivates individuals to continue challenging their fears.
Developing Coping Strategies
Building a repertoire of effective coping strategies is integral to managing anxiety associated with OCD breathing. Mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and cognitive reframing are examples of techniques that individuals can employ in real-time when confronted with obsessive thoughts. Developing a personalized toolkit of coping strategies enhances resilience and empowers individuals to navigate challenging moments with greater ease.
Conclusion
Overcoming OCD breathing requires a comprehensive and personalized approach that addresses the cognitive, behavioral, and emotional components of the disorder. Seeking professional help, embracing therapeutic techniques like CBT and ERP, building a strong support system, and incorporating self-care practices are essential elements of a successful treatment plan. By understanding the nature of OCD breathing and implementing targeted strategies, individuals can reclaim control over their lives and experience lasting relief from the burdens of obsessive-compulsive thoughts related to breathing.
Related Topics:
How Do You Stop OCD Panic Attacks?
Which Antipsychotic Is Best for OCD?
10 Strategies to Curb OCD Panic Attacks