Heart Disease: America’s Leading Cause of Death
Heart disease has consistently been the leading cause of death in the United States, responsible for 21% of all deaths in 2022. This made it the primary killer, surpassing other significant causes such as cancer, unintentional injuries, and COVID-19. With heart disease contributing to one in six deaths nationwide, the need for continued awareness and preventive measures remains urgent.
Historically, death rates due to heart disease have been higher among men than women. Despite this, both genders have experienced a decline in heart disease mortality rates since the 1950s, thanks to advancements in medical care, public health initiatives, and increased awareness of risk factors. However, the geographic disparities in heart disease mortality suggest that more targeted interventions are needed in certain states.
Understanding the Risk Factors for Heart Disease
The risk of developing heart disease can be significantly reduced by addressing known risk factors. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of physical activity, poor diet, and obesity are among the most prominent preventable contributors to heart disease. Notably, states with the highest heart disease death rates often have elevated levels of these risk factors.
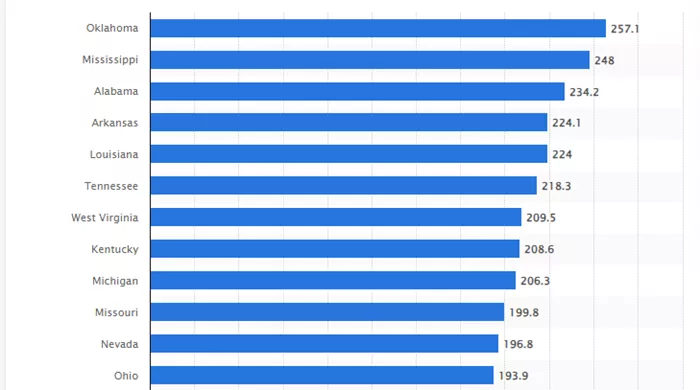
For instance, Oklahoma, which reported the highest heart disease mortality rate in 2022, also ranks third in the nation for obesity. Similarly, Mississippi, which has the second-highest heart disease death rate, leads the country in physical inactivity. These correlations highlight the importance of lifestyle and behavioral factors in the prevalence of heart disease.
The Broader Impact of Heart Disease Across the United States
While states like Oklahoma, Mississippi, and Alabama bear the brunt of heart disease fatalities, the impact of this condition is felt nationwide. The variation in death rates across states reflects differences in healthcare access, socioeconomic factors, and public health initiatives. States with higher death rates often face challenges such as lower healthcare access, higher poverty rates, and less effective public health campaigns.
To combat heart disease on a national level, a multifaceted approach is required. This includes promoting healthier lifestyles, improving access to healthcare, and implementing targeted public health interventions in high-risk areas. By addressing the root causes of heart disease and prioritizing prevention, it is possible to reduce mortality rates and improve overall public health outcomes across the country.
Related Articles:
American Indian Adults Face Dramatic Surge in Heart Failure Rates, New Study Reveals
Health Experts Emphasize Prevention in Reimagining Heart Care
Semaglutide Emerges as a Breakthrough for Kidney and Heart Health in Diabetes Patients