69
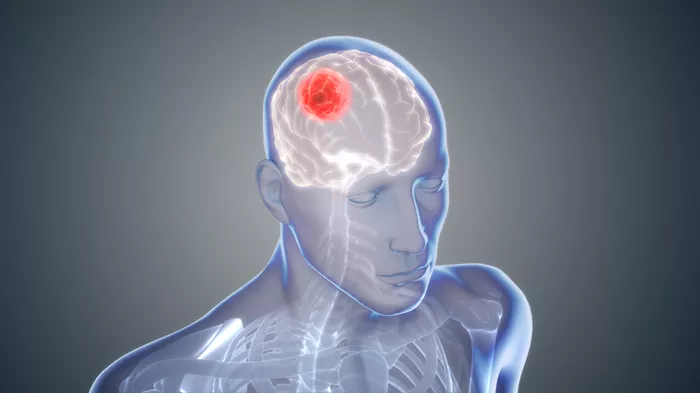
In a groundbreaking development, a collaborative team of scientists from China and the United States has created a novel plant-based nanoparticle treatment for glioblastoma, the most aggressive and rapidly growing form of brain cancer. Researchers from Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University and Yale University have discovered that bardoxolone methyl (BM), a phytochemical capable of forming spindle-shaped nanoparticles, effectively targets and destroys tumor cells in preclinical studies.
Advertisements